Introduction
Meat—both red meat and white meat—remains a cornerstone of diets around the world. It provides concentrated protein, bioavailable iron, zinc, and vitamin B12, nutrients that are critical for growth, repair, and neurological function. Yet in the last decade a large and growing body of research has also linked certain patterns of meat consumption—particularly high intake of processed red meat—to elevated risks of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and colorectal cancer. This article synthesizes current evidence from leading researchers and international agencies, highlights the main nutritional trade-offs, and offers practical, SEO-friendly guidance for choosing, preparing, and balancing meat in a healthy diet. Key scientific findings from Asia, North America, and Europe are cited throughout. Organisation Mondiale de la SantéBMJPubMed
Key points
- Red meat and white meat are rich sources of high-quality protein, heme iron, and vitamin B12—nutrients often harder to obtain from plant-only diets.
- Processed red meat (bacon, hot dogs, cured sausages) has been classified as carcinogenic to humans by the IARC/WHO; unprocessed red meat is considered probably carcinogenic. Organisation Mondiale de la Santé
- Large cohort and meta-analytic evidence links higher red and processed meat intake with greater cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality. Substituting plant proteins, fish, or poultry can lower these risks. BMJPubMed+1
- Food choice is also an environmental and sustainability question: major commissions (EAT-Lancet) recommend reducing global red meat intake for planetary and human health. EAT

Definitions and nutritional basics
Red meat : muscle from mammals (beef, lamb, pork, buffalo). Characterized by higher myoglobin content, giving it a red color, and typically higher levels of heme iron and saturated fat.
White meat : poultry (chicken, turkey) and fish; generally leaner, lower in saturated fat, and in many cases richer in omega-3 fatty acids (for oily fish).
Processed meat : meat transformed through salting, curing, smoking, or chemical preservatives (e.g., nitrites). The IARC links processed meat with colorectal cancer risk. Organisation Mondiale de la Santé
Nutritional benefits : what meat reliably supplies
- High-quality protein (complete amino acid profile) — critical for muscle maintenance, recovery after illness, and for older adults to avoid sarcopenia.
- Heme iron (red meat) — more readily absorbed than non-heme iron from plant sources; important to prevent iron-deficiency anemia.
- Vitamin B12 — essential for DNA synthesis and neurologic health; virtually absent in plant foods without fortification.
- Zinc — required for immune function, wound healing, and growth.
The nutritional value makes meat an important option in many settings—especially where plant diversity or fortification is limited. However, nutrient benefits must be balanced against disease risk patterns associated with high intake of certain meats. PMC

Evidence summary : risks associated with red and processed meat
1. Cancer (colorectal and others)
In 2015 the IARC (part of WHO) classified processed meat as carcinogenic (Group 1) and red meat as probably carcinogenic (Group 2A)—with the strongest evidence for colorectal cancer. The mechanisms proposed include formation of N-nitroso compounds, carcinogenic heterocyclic amines from high-temperature cooking, and iron-mediated oxidative damage. Organisation Mondiale de la SantéPubMed
2. Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Multiple recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses report associations between higher red meat intake and increased risk of CVD events and CVD mortality. A 2023 meta-analysis found both unprocessed and processed red meat were linked to greater CVD risk, with processed meat often showing stronger associations. Dietary patterns that reduce red/processed meat and increase plant foods are associated with lower CVD incidence. PubMedOxford Academic
3. Type 2 diabetes (T2D)
Large prospective cohort research (including multi-decade data analyzed in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition and other journals) shows a consistently positive association between red meat intake—especially processed red meat—and incident type 2 diabetes. Some recent cohorts indicate even modest consumption (e.g., two servings/week) is associated with higher T2D risk; substitution of plant proteins, fish, or poultry is linked to lower risk. PubMedHarvard Chan Santé Publique
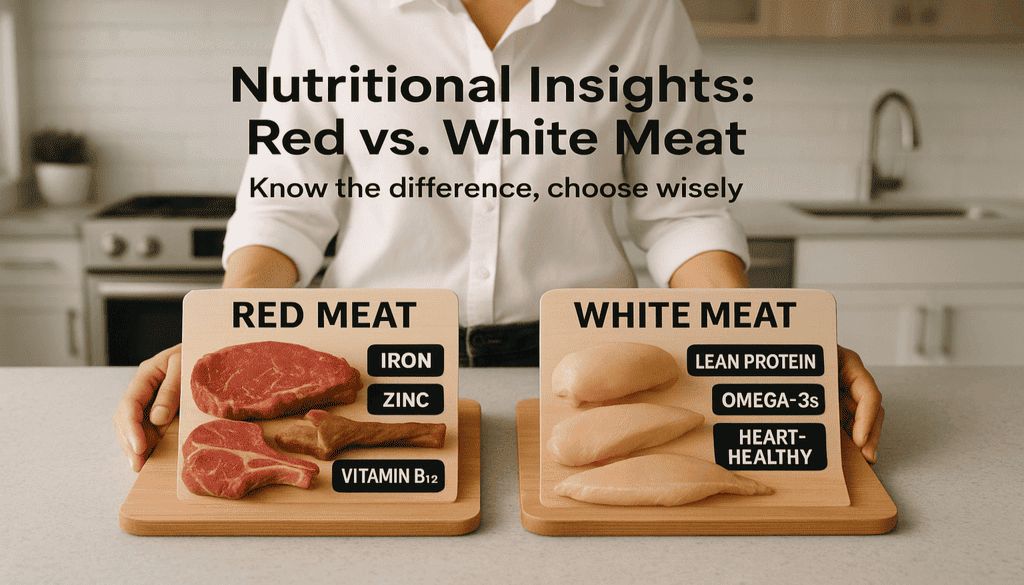
Practical comparison : red vs white meat (quick table)
| Feature / Concern | Red Meat | White Meat |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | High (complete) | High (complete) |
| Heme iron | High (easily absorbed) | Low to moderate |
| Saturated fat | Often higher | Generally lower |
| CVD / T2D association | Stronger associations at high intakes | Lower risk profile (esp. fish/poultry) |
| Cancer risk (processed) | Processed red meat = carcinogenic | Mostly not classified as carcinogenic |
| Best choices | Lean cuts, limit processed forms | Skinless poultry, oily fish (salmon, mackerel) |
Cooking and selection : reduce risk with smart choices
- Prefer unprocessed, lean cuts (e.g., sirloin, round). Trim visible fat.
- Limit processed meats (bacon, hot dogs, many deli meats). If you consume them, do so rarely. Organisation Mondiale de la Santé
- Use low-temperature methods (braising, stewing, steaming) rather than charring/grilling at high heat to reduce heterocyclic amine and PAH formation.
- Increase fish, poultry, legumes, nuts, and whole grains as protein replacements on some days of the week. Cohort studies show that substituting plant proteins or fish for red meat reduces mortality and chronic disease risk. PMCPubMed
Evidence from prominent researchers and commissions
- Walter Willett, M.D. (Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health) — co-author of the EAT-Lancet discussions and a leading voice in epidemiologic diet research advocating reduced red meat consumption for health and sustainability. EATPortail de recherche de Groningue
- Frank Hu, M.D., Ph.D. (Harvard) — key author in cohort research linking red and processed meat to CVD, diabetes, and mortality; has emphasized substitutions (nuts, fish, poultry) for red meat. Harvard Chan Santé PubliqueAARP
- W. Shi et al. (2023) — European Heart Journal meta-analysis summarizing associations between red meat and cardiovascular disease across multiple cohorts. PubMed
- IARC / WHO expert group (2015) — international evaluation that categorized processed meat as carcinogenic and red meat as probably carcinogenic. Organisation Mondiale de la Santé
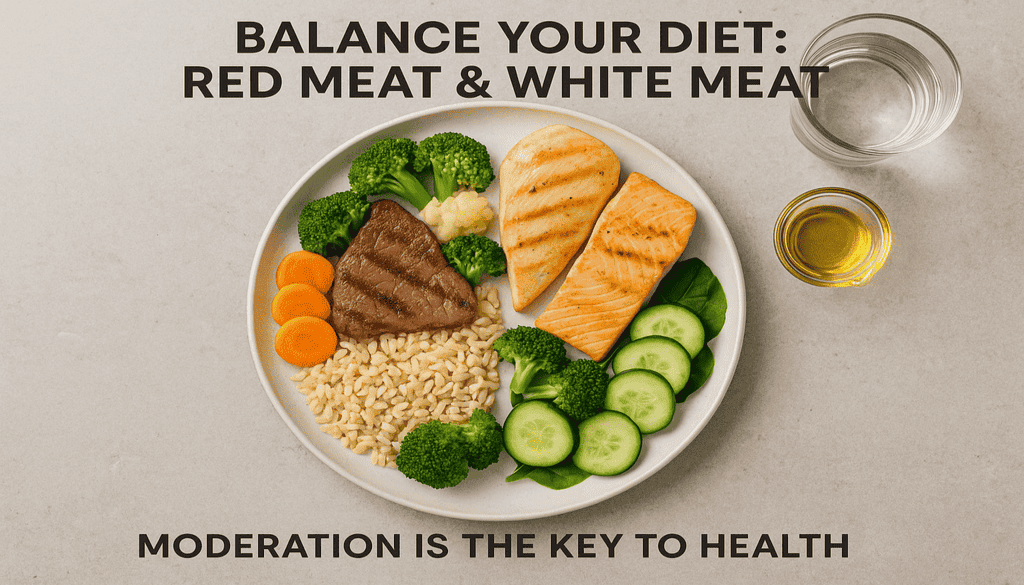
Practical recommendations (evidence-based)
- Keep processed meat intake to a minimum or avoid it whenever possible. Organisation Mondiale de la Santé
- Limit unprocessed red meat to moderate amounts—many public health reports suggest around 300–500 g (cooked weight) per week or less as a reasonable target for health and environmental reasons; replace some servings with fish, poultry, legumes, or nuts. EATAHA Journals
- Favor oily fish (source of omega-3s) and plant proteins to improve cardiometabolic profiles. PubMed
- Use healthier cooking methods and minimize charring; choose lean cuts and trim fat.
Figure suggestion (for article or infographic)
- Figure idea: Stacked-bar showing relative risk (%) for colorectal cancer, CVD, and T2D across quintiles of processed red meat intake (data synthesized from IARC and cohort meta-analyses). Caption: Relative risk increases with higher processed meat intake; substitution with plant proteins reduces risk. (Data sources: IARC 2015; Zheng et al. BMJ 2019; AJCN 2023). Organisation Mondiale de la SantéBMJPubMed
Conclusion
Red and white meats supply concentrated, high-value nutrients—protein, iron, zinc, and vitamin B12—and can be part of a healthy diet. However, a large and consistent body of international research shows that regular, high consumption of red and especially processed red meat is associated with higher risks of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and colorectal cancer. Leading health organizations and research teams in Asia, North America, and Europe (including WHO/IARC, Harvard researchers, and recent meta-analyses) recommend moderating red meat intake, minimizing processed meats, and increasing plant-based proteins and fish/poultry as healthier substitutes. Adopting these moderate, evidence-driven strategies helps protect long-term personal health while also supporting more sustainable food systems. Organisation Mondiale de la SantéBMJEAT
Select references (representative)
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Q&A: Carcinogenicity of the consumption of red meat and processed meat. WHO/IARC (2015). Organisation Mondiale de la Santé
- Zheng Y., et al. Association of changes in red meat consumption with total and cause-specific mortality: results from cohort studies. BMJ. 2019. BMJ
- Shi W., et al. Red meat consumption, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European Heart Journal (2023). PubMedOxford Academic
- Zeraatkar D., Johnston BC., et al. Effect of lower versus higher red meat intake on cardiometabolic and cancer outcomes: systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2019. PMC
- Gu X., et al. Red meat intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in prospective cohorts. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2023). PubMed
- Willett W., Rockström J., et al. EAT-Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. EAT-Lancet (2019). EAT
- Lichtenstein AH., et al. AHA Scientific Statement – Dietary guidance to improve cardiovascular health (2021). American Heart Association. AHA Journals





